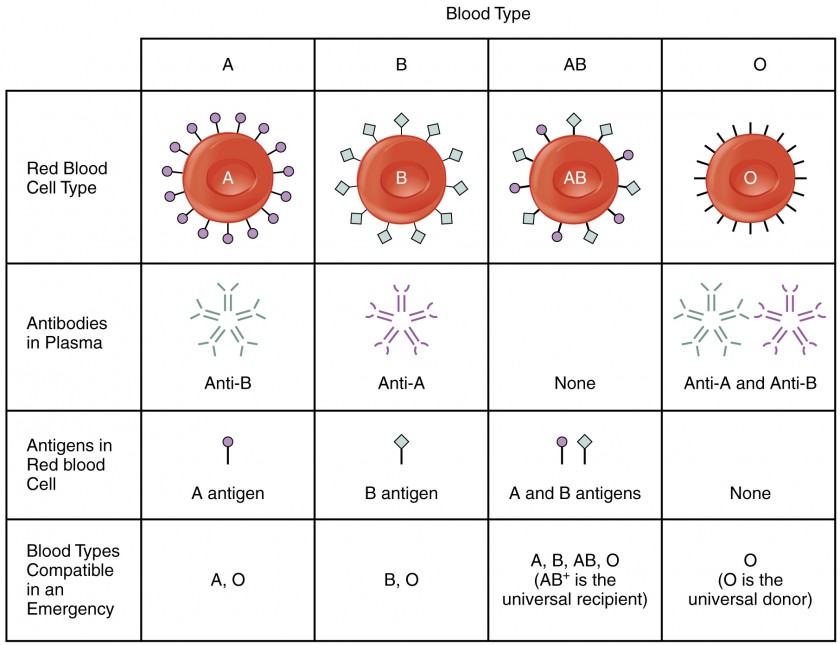
Anti-A antibody and Anti-B antibody. Foreign antigens originate from outside the body.

Pdf Blood Groups And Red Cell Antigens Bizuayehu Hafebo Academia Edu
Because cancer cells often use more glucose than normal cells the pictures can be used.
. Plural for cells that eat bacteria and fungi. Plural for white blood cell. An antibody is defined as a large Y-shaped protein that is used by the immune system to identify and neutralize pathogens such as bacteria and viruses.
Antigens could be anything like a pathogen or bacteria or fungi or even virus. An antigen is thought to be any foreign. Antigen - A substance on the surface of red Blood cells that elicits an immune response when transfused into a patient who lacks that antigen.
Depending on which of these genetically determined proteins or antigens known as red blood cell antigens you inherited you will have. Antigens that they lack on their own RBCs alloantibodies following exposure to foreign RBC antigens through blood transfusion or pregnancy. Donor and recipient blood types are A positive.
A positron emission tomography PET scan is a process where a small amount of radioactive glucose sugar is injected into a vein and a scanner is used to make detailed computerized pictures of areas inside the body where the glucose is used. It is used to describe a foreign molecule which generates an immune response- antibody generator- substances that generate an immune response. For example blood type A has antigens.
It is cause by sialic acid groups on the red blood cell membrane which gives the cells a negative charge. They cause diseases or allergic reactions. They attack micro organisms in the body and surround the micro organism and digest them just like amoeba takes in its food these white blood cells are called phagocytes and the process they carry out is called phagocytosis.
Antiserum - Human Blood serum containing antibodies that are specific for one or more antigens. These antigens create specific antibodies that will take specific blood types. In general two main divisions of antigens are recognized.
Agglutinate with anti-A sera and Agglutinate with anti-B sera. The positive ions in saline attracted to the negatively charged red blood cells. Antigens are substances that stimulate the immune system to produce antibodies.
Blood cells contain antigens attached to the outside membrane of the cell. The proportion of patients with. Antigens are generally proteins.
5 PET Positron Emission Tomography. Zeta potential refers to the repulsion between the red blood cellsIt is due to an electric charge surrounding cells suspended in saline. ANTIGENS The term antigen is used in two senses.
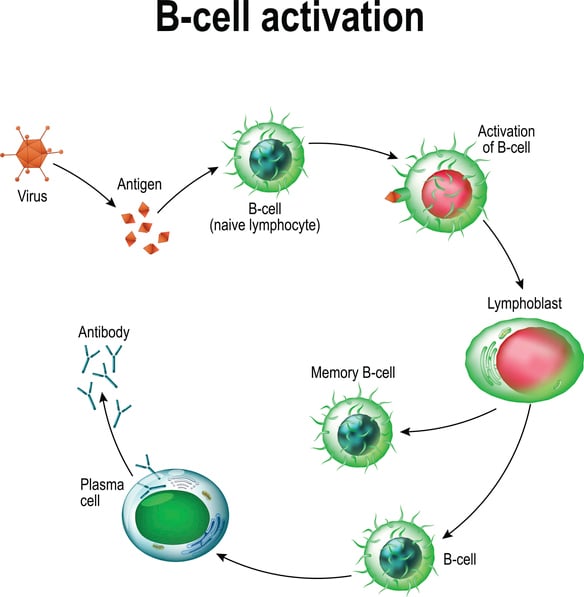
Antigen substance that is capable of stimulating an immune response specifically activating lymphocytes which are the bodys infection-fighting white blood cells. Thus there is a resultant effect of a specific response. Antibodies are produced and released in the body as a result of antigen stimulation.
The bodys integrated response to an antigen mediated by lymphocytes. Severe immune-mediated transfusion reactions usually involve the humoral arm. Antinuclear Antibody - ANA basically a test for lupus and other auto-immune inflammatory diseases.
Humoral using antibodies and cellular using immune cells. Foreign antigens or heteroantigens and autoantigens or self-antigens. The bodys integrated response to an antigen mediated by lymphocytes.
Each antigen has a distinct surface feature or epitope. The antibodies they produce bind to the antigen. There are two main arms of immune response.
They are specific to the antigen that stimulated their production. In this capacity it is called an immunogen. In the case of a foreign red blood cell.

Week 11 Blood Typing Flashcards Quizlet

Lesson Explainer Structure And Function Of Antibodies Nagwa




0 Comments